Scanning Name
CT TEMPORAL BONE
Reports
Fast report turn around time
Laboratory Professionals
Specialised clinical reports by experts
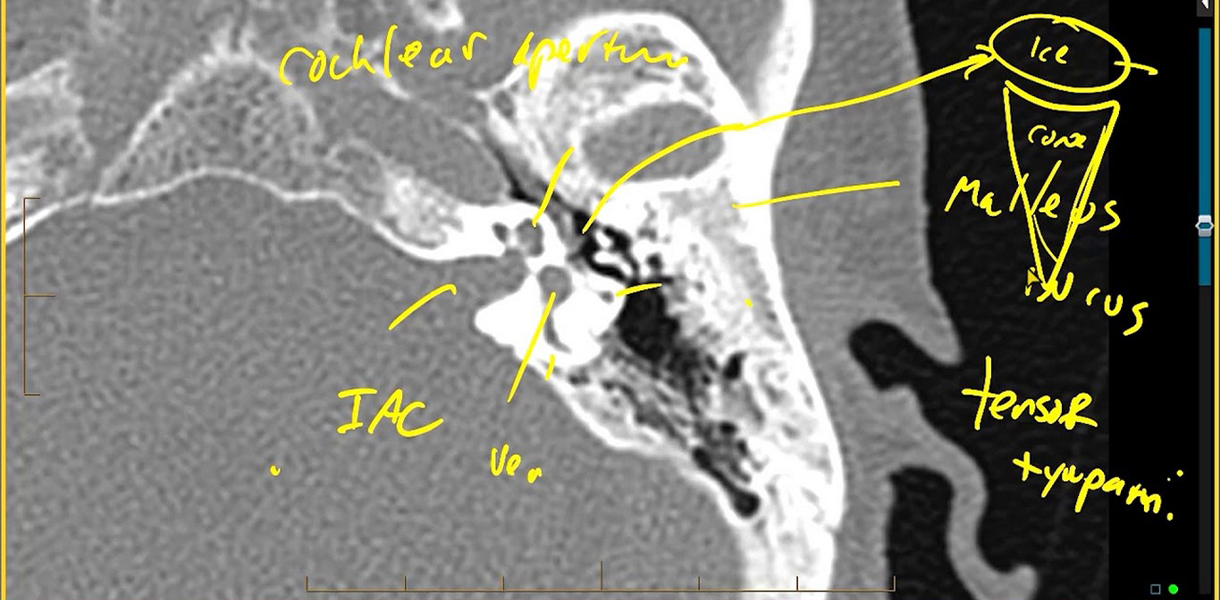
CT Temporal Bone Imaging
CT Temporal Bone Imaging is a diagnostic procedure used to evaluate the structures of the temporal bone, including the ear canal, middle ear, inner ear, and adjacent structures. It helps in diagnosing various ear and temporal bone conditions.
Process:
During a CT Temporal Bone scan, the patient lies on a table that moves into the CT scanner. The scanner captures detailed cross-sectional images of the temporal bone using X-ray technology. These images provide comprehensive views of the bony structures and soft tissues of the ear and surrounding areas.
Uses:
- Diagnosis of Conductive Hearing Loss: CT imaging helps in identifying causes of conductive hearing loss, such as middle ear infections or structural abnormalities.
- Assessment of Inner Ear Disorders: It aids in diagnosing conditions affecting the inner ear, including labyrinthitis, vestibular schwannoma, or Meniere's disease.
- Evaluation of Temporal Bone Trauma: CT scans can detect fractures or injuries to the temporal bone resulting from head trauma.
- Detection of Cholesteatoma: CT Temporal Bone imaging is instrumental in diagnosing cholesteatoma, a non-cancerous growth in the middle ear.
- Preoperative Planning for Ear Surgery: Otolaryngologists use CT images for planning surgical procedures, such as tympanoplasty or mastoidectomy.
Others:
- Comprehensive Visualization: CT Temporal Bone imaging provides detailed views of complex ear anatomy, facilitating accurate diagnosis and treatment.
- Guidance for Ear Procedures: CT findings assist ENT specialists in determining appropriate treatment strategies for ear and temporal bone disorders.
- Patient Comfort: The procedure is well-tolerated and does not require extensive preparation.